If you’re looking for a dermatologist “near me,” you’re likely already curious about ways you can better care for your skin. Did you know that your skin is the largest organ of your body? That’s one reason why proper skin care is so important to our overall health—and a large reason healthy adults regularly visit a dermatologist. But what is a dermatologist exactly?
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases. Acne, skin cancer, psoriasis, and eczema are just a few of the conditions that dermatologists treat on a daily basis. In this article, we will answer some of the most frequently asked questions people have about dermatology. We will explain what a dermatologist is, what they do, how they treat acne, why skin health is so important, and more!
What Is a Dermatologist?
Dermatologists are doctors who have studied conditions affecting, nails, hair, and skin. Regular visits to your dermatologist can protect you from developing diseases in these areas of your body and treating those that do occur.
What Diseases Do Dermatologists Treat?
There are over three thousand different diseases of the skin, nails, and hair that a dermatologist may be licensed to treat. Ranging in severity from vitiligo to epidermolysis bullosa, a dermatologist will be able to diagnose skin rashes, irritation, and irregularities and suggest the appropriate treatment for them.
Can Dermatologists Be Specialists?
In addition to the regular schooling required to become a dermatologist (four years of college, four years of medical school, one year of internship in a related field, three years of residency, an optional year or two of fellowship, and finally licensing and certification), some dermatologists will dive deeper into certain conditions or age groups and specialize in their field. Subspecialists range in specialty from:
- Cosmetic dermatology
- Pediatric dermatology
- Mohs surgery, or skin cancer surgery
- Dermopathology, or the study of skin diseases
- And others
Do Dermatologists Treat Hair Loss?
The short answer to this question is yes, dermatologists will diagnose and treat hair loss and hair thinning—in both men and women.
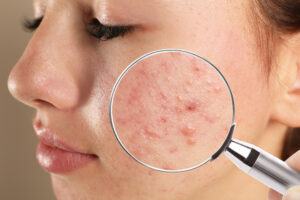
How Do Dermatologists Treat Acne?
Up to 50 million Americans struggle with acne each year, making it the most common skin condition in the country. However, there is no one-size-fits-all solution for treating acne, as each person’s circumstances, triggers, and responses to medications are different. Here are some of the common ways dermatologists treat acne:
- Oral medications: There are a wide number of different oral medications dermatologists may prescribe depending on each patient. Some common oral medications for acne include:
- Antibiotics: The idea behind antibiotics is to reduce the amount of acne-causing bacteria. This, however, is not an ideal solution because there is the potential to create antibiotic resistance. As such, it is often used in tandem with other approaches, such as benzoyl peroxide, to reduce this risk. Antibiotics will also increase a patient’s sensitivity to UV light.
- Anti-androgen compounds: If antibiotics are yielding limited results, anti-androgen agents may be prescribed to teenage girls and adult women in order to blog the effect of androgen hormones on the skin’s oil-producing glands. This can, however, cause painful menstruation and breast sensitivity.
- Isotretinoin: This synthetic version of vitamin A is often prescribed for people with severe acne that does not respond to other treatments. Potential side effects can include birth defects, depression, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Oral contraceptives: Some oral contraceptives have been approved by the FDA to lessen acne in addition to acting as birth control. These contraceptives are frequently prescribed in addition to other acne medications or topical creams as well. Side effects include nausea, increase in weight, breast sensitivity, and an increased risk of cervical and breast cancer or cardiovascular problems.
- Skin therapies: Whether performed at your local spa or at your licensed dermatologist, there are some forms of skin therapies that have proven to be effective against some types of acne. These are usually best applied with other medications for better results. Therapies an acne patient might try include:
- Blackhead, whitehead, or cyst removal: Using a steroid injection or special metal tools, a dermatologist will gently remove comedos or cysts that are resistant to topical medications. While this may improve the appearance of your skin, there is also a danger of causing scarring—which is why so many dermatologists do not recommend attempting this type of procedure yourself at home.
- Chemical peels: Usually through the process of applying a thin layer of either retinoic, glycolic, or salicylic acid, this mild acne treatment will often improve the superficial appearance of the skin, but results are short-lived and the procedure must be repeated for continued results.
- Light therapy: This form of acne treatment is still being studied, but some patients have experienced success with light exposure. Further clinical trials are needed to conclusively solidify this form of treatment.
- Topical solutions: This is a common approach to treating acne as it tends to have milder, more manageable side effects. Common topical solutions for treating acne include:
- Antibiotics: Often used in tandem with a retinoid cream, an antibiotic cream will skill excess skin bacteria, reduce inflammation, and lessen redness. These creams are also often prescribed with benzoyl peroxide to lessen the likelihood of antibiotic resistance—and using this approach to treating acne on its own is not recommended.
- Azelaic and salicylic acid: With antibacterial properties, an azelaic acid topical solution will often be prescribed for use twice a day. This form of treatment can be an option for women who are pregnant or are breastfeeding, though it may cause skin irritation or redness.
- Dapsone: This form of treatment is prescribed for twice-daily application for inflammatory acne, especially in women. Side effects include skin irritation, dry skin, and redness.
- Retinoids: These trugs often come as a cream or a gel and works by preventing the hair follicles from plugging. This should not be applied in tandem with benzoyl peroxide. Topical retinoids will make your skin more sensitive to UV light, and can cause redness, irritation, and dry skin.
With so many different resources for treating acne, it may take some time with the right dermatologist before you find the right solution for your skin. The important thing to remember is that there are plenty of options, and working with your dermatologist to dial in your acne treatment can be a very rewarding endeavor!
What Kinds of Procedures Will Dermatologists Do?
Dermatologists do so much more than just treating acne, however. In fact, there are all sorts of procedures a dermatologist might do on any given day of the week. Here are some common types of procedures a dermatologist will perform:
- Cryosurgery, or the use of extremely cold temperatures to freeze and permanently damage tissue.
- Electrosurgery, or the use of a high-frequency electric current to incise or damage tissue.
- Excision surgery, or the use of a scalpel to cut and remove tissue with appropriate measures for closing the wound.
- Laser surgery, or the use of a laser to perform precise surgical procedures.
- Mohs surgery, or a layer-by-layer removal of cancerous skin cells from your dermis.
- Mole removal, whether partial or complete, involves removing a mole to determine if it is cancerous or a result of some other skin disease.
- Vein treatment, or the use of sclerotherapy or laser treatments to rehabilitate damaged veins.
Dermatologist Near Me
It can seem like a little acne is no big deal—but your skin is your first line of defense against all the dangerous pathogens from the outside world, including fungus, viruses, bacteria, dirt, and even tough materials that may cause lacerations or abrasions! If left untreated, skin conditions can often worsen and spread—and in the case of melanoma, they can even be fatal. If you suspect you have a skin condition that warrants professional attention, don’t wait. Setting up regular visits with a dermatologist is a foundational aspect of properly caring for yourself.
Are you looking for a “dermatologist near me”? Contact the National HealthCare Center today to schedule an appointment!